This website uses cookies to facilitate navigation, registration and collection of statistics. The information stored in cookies is used exclusively by our website. When browsing with active cookies consents to its use.
Canada’s ASD industry is expected to grow mainly due to strong Defense sector performance and free trade agreements with the EU
Canada ASD industry overview
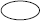 2012-17 CAGR
2012-17 CAGR
| The Canadian ASD industry grew by 4,9%/ year, reflecting an increase of 0,4 pp in % GDP (2012-17) |
Canadian ASD revenues [€bn, 2012-17]
- The Canadian ASD industry market growth is mainly due to the anticipated increase of aircraft orders and Defence manufacturing
- The Space sector is starting to have a significativeweight in the total ASD market, with the government increasing its investments in order to follow the global communication systems demand
| Satellite communication and navigation systems are the main drivers for continuing growth |
Aeronautics
- Canada is investing €700m to develop a regional ecosystem for commercial and civil UAV (1)due to its global market anticipated growth of 18,2% between 2017 and 2023
- The projected increase of aircrafts by 2036 will lead to a 3k pilot shortage by 2025, with the government planning a €150 million investment in training
Space
- Space sector is a government priority, investment of €11,5 million to develop a advanced satellite broadband network to improve global communication systems
- Commercial market dominates, forecasted to reach €250 billion by 2023 (+40%) due to satellite communications and SatNavmarket revenues growth
Defense
- Government is investing €41,2 billion in new funding over the next 20 years to the Defense budget in order to develop 88 new fighter jets and ground-base Defense solutions
- National focus of reducing supply costs led to the 2017 Canada’s agreement decreasing up to 98% of trade tariffs between Canada and Europe
Note: (1) UAS –Unnamed Aerial Space
Sources: DIME, Aeró Montréal, GMIS, State of Canada, ForecastInternational, Bombardier, EY analysis
Canada has been mostly focused in the Aeronautics sector and in increasing its domestic sales to meet the national needs
Canadian ASD industry: revenues and workforce zoom-in
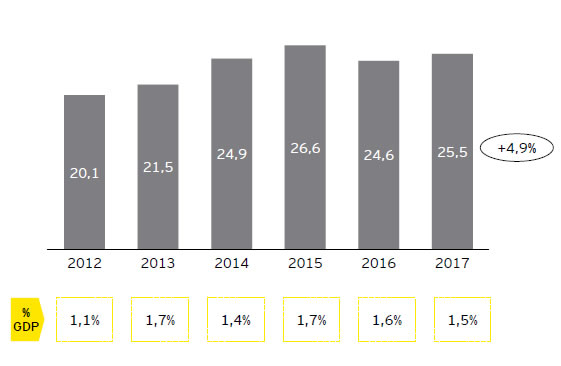
| The Canadian industry is highly focused in the Aeronautics sector representing 86% of the total national revenues |
Canadian ASD industry revenues by sector [% of total revenues, 2017]
- The Canadian Defense sector represents only 12% of the total ASD industry due to (in part) strong competition from the US
- The Space sector is the less representative of the ASD industry and composed of SMEs that create 45% of the total Space sector revenues
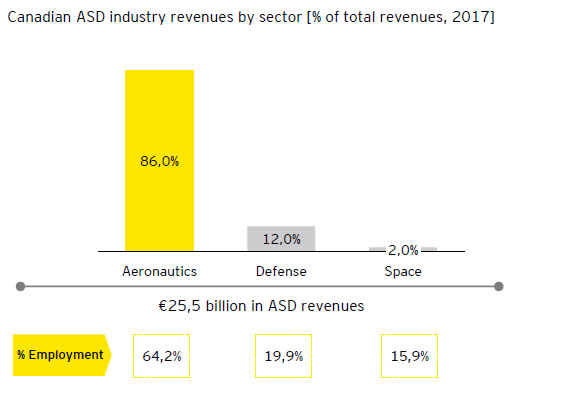
| Domestic sales have been increasing and represent 48% the total industry revenues, raided mostly by the presence of an OEM |
Canadian ASD market breakdown by revenues [% of €bn, 2016-17]
- More than half the total Canadian employees represent a low-mid value-added but highly specialized workforce
- On the other hand, 26% of the total Canadian employees are included in the STEAM category, representing an high value-added workforce responsible for R&D activities
Notes: (1) STEAM -Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics; (2) Includes management, administration, marketing, and unspecified occupations
Sources: AIAC, State of Canada, EY analysis
